
Chiropractor Chandler AZ
PRP PROLOTHERAPY VS STEM CELLS FOR KNEE MENISCUS
Knee meniscus is a piece of cartilage that acts as a cushion and provides support to the knee joint. It also helps in distributing the pressure of weight evenly within the knee. There are two menisci in the knee joint which provide a cushion between the thighbone (femur) and shinbone (tibia). The meniscus can easily be damaged if too much pressure is put on the knee joint or it is rotated suddenly. According to the Boston Children's Hospital, more than 500,000 meniscal tears are reported in the U.S. each year. A meniscal tear can make it difficult to perform daily activities and causes pain.

The knee meniscus tear is caused by sudden pressure on the knee due to a forced rotation or twist. A sudden turn, deep squat or heavy weight lifting can lead to a meniscus tear. Many athletes that are involved in sports which require sudden stops or turns are at a higher risk of knee meniscus tear. According to Boston Children's Hospital, the prevalence of meniscus tear is increasing in young children because of their increased participation in organized sports like football, basketball, and tennis.
People over the age of 30 are at a higher risk for a meniscus tear since the meniscus weakens with age.
Osteoarthritis is a joint degenerative disease that leads to meniscus weakening and pain in the knee. People with osteoarthritis are at higher risk of having a meniscus tear as they have a weak meniscus.
SYMPTOMS OF KNEE MENISCUS TEARWhen the meniscus tear occurs, the person may hear a cracking sound in the knee. After that, he/she can experience some of the following symptoms:
- Pain at touching the knee joint
- Swelling around knee joint
- Difficulty in knee movement and rotation
- Knee lock
- Knee unable to support the weight of the body
DIAGNOSIS OF KNEE MENISCUS TEAR
Physical ExaminatAfter knowing the symptoms, the doctor will perform a physical examination of the knee by testing the range of motion. The McMurray Test will also be performed by the doctor in which the doctor will bend your knee and then straighten it and rotate it.
Imaging TestsImaging tests can also be performed to confirm the meniscus tear. These include X-ray and MRI. An X-ray will not confirm the meniscus tear but it will help to determine if there is any other cause of pain in the knee. MRI will provide a picture of cartilage and ligaments in the knee to confirm if the meniscus is damaged or not.
ArthroscopyIf the cause of knee pain is not determined by mentioned above physical examination and imaging tests, arthroscopy is performed especially if surgery is required.
TREATMENT OF KNEE MENISCUS TEARConventional methods for treating a knee meniscus tear are ice, heat, rest, physical therapy and medication. Physical therapy helps in reducing pain and increasing mobility and knee rotation. To reduce the swelling in the knee, medication such as ibuprofen, aspirin, or any other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAID) medication is prescribed. The recovery time for conventional treatment can vary from 1-3 months.

Surgery is recommended when the meniscus tear fails to respond to the conventional treatment methods. Arthroscopic surgery takes around one hour in which the damaged meniscus is repaired or trimmed.
Surgery involves many risks and minimal long term benefits. It also requires regular doctor visits and regular physical therapy to strengthen the muscles supporting the knee joint.
Knee meniscus is an avascular cartilaginous structure that requires sufficient supply of nutrients to heal. Surgery is unable to stimulate the healing of meniscus and rather has the opposite effect. Therefore, a method that can stimulate the self-healing in meniscus is more valuable in treating a meniscus tear.
ALTERNATIVE TREATMENT OPTIONSResearch is going on to discover alternative treatment options that can use the self-healing properties of the body to treat the injury. Prolotherapy is one of the alternative treatment options that fulfills this requirement. Prolotherapy is a short form of proliferation and therapy and it manipulates the body's repair machinery to repair the damage. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) Prolotherapy and Stem cell plasma Prolotherapy are two types of Prolotherapy that are very effective in treating the knee meniscus tear.
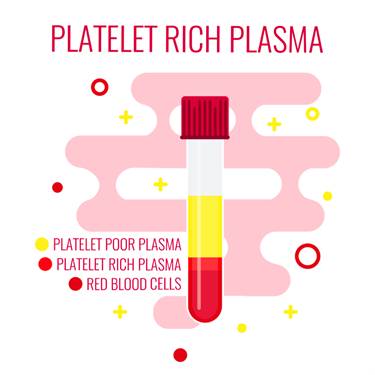
Platelet-rich plasma Prolotherapy uses the blood of the patient to treat the damage. The blood contains platelets that have a role in tissue repair. Platelets contain alpha granules which contain growth factors. In PRP Prolotherapy, the blood is drawn from the patient and centrifuged to separate different components of the blood. The platelet-rich plasma is separated from other layers. This is then injected back into the patient at the site of injury.
When platelets are injected, they get activated and release the alpha granules. Alpha granules secrete a lot of growth factors at the injury site. Higher than normal levels of alpha granules attracts the repair proteins and stem cells at the injury site to accelerate the repair process. These repair proteins and stem cells repair muscles, bones, ligaments and tendons at the injury site, relieve the pain and also keep the structure of the joint intact.
In platelet-rich plasma Prolotherapy, the blood of the patient is used to derive the platelets hence there is no risk of blood-borne disease transfer and allergic reaction. Research has shown no link between PRP Prolotherapy and tumor formation and genetic mutation.
Platelets derived growth factors are studied for their effects in meniscus tear in sheep. The results showed an increase in cell proliferation and extracellular collagen matrix formation in each of the inner, middle, and outer regions of sheep menisci after injecting platelets derived growth factors. After one week, 800% increase was observed in the inner vascular zone as compared to the control group. Collagen production was also increased in the inner and outer meniscus.
Growth factors have shown in various studies to stimulate the healing in the knee meniscus that leads to damage repair and a decrease in pain. Clinical studies have shown that PRP Prolotherapy is effective for treating meniscal tears in the knee and can be considered as a first-line treatment for meniscal injuries.
Stem cell Prolotherapy is another type of Prolotherapy that uses adult stem cells of the patient to repair the damage in the body. Adult stem cells are present in all the tissues of the body in a different amount and the major reservoir is in fat tissues and bone marrow. Adult stem cells are derived from fat tissues or the bone marrow and grown in the laboratory to increase the cell count. Adult stem cells are considered to be able to differentiate into any type of specialized cell in the body when injected back into the body at the injury site.
In stem cell Prolotherapy, when the stem cells are injected, they differentiate into the native cells and signals the local stem cells and repair proteins to start the repair process. Stem cells also suppress inflammatory T–cell proliferation and provide an anti-inflammatory effect that is helpful in the case of the inflammatory degenerative disease.
In 2011, a study was performed which showed that the undifferentiated adult stem cells are capable of producing bone, ligaments, tendons and cartilage. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) are used in the stem cell Prolotherapy. MSCs have shown in-vitro to differentiate and help in healing different varieties of musculoskeletal injuries. These include cartilage repair, tendon and ligament repair, intervertebral disc repair, tendon defects repair and angiogenesis.
In 2003, significant improvement in cartilage regeneration was reported in animal models after using adult stem cells. It not only showed great improvement in meniscus regeneration but also reduced the progressive destruction of cartilage in degenerative diseases.
In 2008, a research study showed significant knee cartilage growth and symptom improvement in a human case study report using adult stem cells derived from bone marrow.
A study performed on osteoarthritis patients showed a visible improvement in cartilage after 6 months of stem cell injections. Another study also showed similar results when the stem cell injection was administered to treat knee meniscus tear. It showed an increase in cartilage and meniscus volume with an improvement in the motion range and a better pain score.
Platelet-rich plasma Prolotherapy and Stem cell Prolotherapy are two very advanced techniques that are promising in knee meniscus repair when the conventional methods fail. They both have shown great results in both in-vitro and in-vivo studies and research is still going on to establish their effectiveness. Both methods are not FDA approved and more research is required to achieve this milestone. It is considered to be more effective to use PRP and stem cells together to attain maximum results in adverse cases. In mild cases, PRP Prolotherapy can give positive results and, in more damaged cases where cartilage is completely destroyed or damaged, stem cell Prolotherapy or a combination therapy will be effective.
Conservative Treatments to Combine with PRPWhile PRP and stem cell treatments are enhancing the tissue repair and regeneration, conservative treatments can enhance healing, strengthen the muscles, and stabilize joint movements to maximize your recovery.
Cold Laser Therapy Treatments
- ACCELERATED TISSUE REPAIR AND CELL GROWTH
- FASTER WOUND HEALING
- REDUCED FIBROUS TISSUE FORMATION
- ANTI-INFLAMMATION
- PAIN RELIEF
- INCREASED BLOOD FLOW
- INCREASED REPAIR AND REGENERATION
- NERVE FUNCTION AND REPAIR
- INCREASED ENERGY PRODUCTION - ATP
Photons of light from lasers penetrate into tissue and accelerate cellular growth and reproduction. Laser therapy increases the energy available to the cell so it can work faster, better, and quickly get rid of waste products. When cells of tendons, ligaments, and muscles are exposed to laser light they repair and heal faster.

Laser light increases collagen production by stimulating fibroblasts. Collagen is the building block of tissue repair and healing. Laser therapy increases fibroblast activity and therefore collagen production to speed healing.
Low level laser therapy decreases scar tissue formation. Scar tissue can be a source of chronic pain and poor healing. By eliminating excessive scar tissue and encouraging proper collagen production, painful scars and chronic pain is reduced.
Laser therapy causes vasodilatation (increases size of capillaries) which increases blood flow. The treatments also increases lymphatic drainage to decrease swelling or edema. Therefore, laser therapy reduces swelling caused by bruising or inflammation while speeding the recovery process.
Cold laser therapy decreases pain by blocking pain signals to the brain. Some nerve cells sense pain and send signals to the brain. Chronic pain can be caused by overly active pain nerves. Specific wavelengths help "shut off" the pain signals, thereby eliminating your pain.
Low level lasers are excellent at decreasing inflammation, which also increases pain nerve activity. Cold laser therapy also increases endorphins and enkephalins, which block pain signals and decreases pain sensations. Overall, laser therapy reduces painful nerve signals and reduces your perceived pain.

Blood carries nutrients and building blocks to the tissue while carrying waste products away. Increased blood flow to tissues increases and enhances cellular healing. Cold laser therapy increases the formation of capillaries in damaged tissues. Specific laser frequency also increases blood flow to the area treated to enhance injury repair.
Low level lasers increase enzyme activity to improve metabolic activity which affects cell repair and regeneration. The enzymes are turned on "high" to speed the healing.
Nerves heal very slowly. Lasers speed up this process. Damage to nerves causes numbness, pain, muscle weakness, and altered sensations. Laser therapy treatments enhance nerve function, healing, and reduce pain.
ATP is like gasoline for cells, it is the energy source that cells operate. Injured cells often have low levels of ATP, which decreases their ability to heal and repair. By increasing ATP and "gasoline storage levels," cells have more ability to heal and repair.
Therapeutic treatments for addressing soft tissue injuries involve massage therapy, manual therapy, trigger point therapy, Graston Technique, or Active Release Technique. These treatments increase blood flow, decrease muscle spasms, enhance flexibility, speed healing, and promote proper tissue repair.
When these treatments are incorporated into a treatment plan, patients heal faster and are less likely to have long-term pain, soft tissue fibrosis, or scar tissue in the injured muscle. These soft tissue treatments are incorporated with therapeutic exercises and flexibility programs.
Many leg injuries are associated with radiating pain. The two legs function as a system for movement. Injuries in one area of the system are commonly associated with poor joint stabilization in the foot, knee, or hip. This leads to poor alignment and excessive forces being placed onto muscles and tendons. Knee injuries are common because of weakness and poor stabilization of the leg and hip muscles. The combination of muscle weakness, poor coordination, and altered gait mechanics produce excessive strain on the soft tissues.

The lower extremity works as a comprehensive unit performing many of the repetitive tasks at home, work, and recreational sports. Injuries to one area of the musculature often indicate that additional damage has been incurred by other muscles.
Many therapeutic exercises can help restore proper strength and endurance to the leg muscles. Isometric exercises are often the initial treatment exercises. Followed by single plane rubber band exercises for hip, knee, and ankle; flexion, extension, adduction, abduction, circumduction, inversion, and eversion. Dynamic exercises involving stability foam, rubber discs, exercise balls, and BOSU balls can be performed on the floor. The more unstable the surface, the more effort and stabilization is required of all the lower extremity muscles.
Vibration plates enhance neuromuscular learning throughout the ankle, knee, foot, hip, and back muscles. Additional strength exercises can be found on the hip, knee, and foot strengthening pages. More information for injuries and treatments foot pain and exercises.
BIBLIOGRAPHY:
Oliver, K. S., Bayes, M., Crane, D., & Pathikonda, C. (2015). Clinical Outcome of Bone Marrow Concentrate in Knee Osteoarthritis. Journal of Prolotherapy, e937-e946.
Hauser, R. A., Phillips, H. J., & Maddela, H. (2010). Platelet Rich Plasma Prolotherapy as First-line Treatment for Meniscal Pathology. Practical Pain Management.
Lubis, A. M., & Lubis, V. K. (2012 ). Adult bone marrow stem cells in cartilage therapy. Acta Med Indones, 62-8.
Mehrabani, D., Jaberi, F. M., Zakerinia, M., Hadianfard, M. J., Jalli, R., Tanideh, N., et al. (2016 ). The Healing Effect of Bone Marrow-Derived Stem Cells in Knee Osteoarthritis: A Case Report. World J Plast Surg, 168–174.